- Local Time: 12:07 AM
- Weather: 28 ℃ / 83 ℉

Ancient Egyptian symbols affected life in ancient Egypt which was a fusion between the spiritual and the physical aspects that became the foundation of their culture that showed in the form of artistic architecture, symbols, amulets, and many objects that were used to bring good fortune and protection. These ancient Egyptian Symbols played a vital role in passing the culture from one generation to another, as they were written on temple walls & obelisks and used in magical and religious rituals for both the living and the dead. The ancient Egyptians believed that their earthly presence was only a part of their eternal voyage and that death was only the beginning of a new chapter in another realm.
Egypt Tours can be your own magical symbol that will lead you all across the incredible destination of Egypt like Cairo, Alexandria, Luxor, and Aswan where the ancient knowledge of the ancient Egyptian civilization is located. The Egyptian symbols were depicted in the form of hieroglyphs and treated as “The Words of Gods” which were used to document the most important events in ancient Egyptian History, their spiritual beliefs, and culture.
Ancient Egyptian symbols were a fusion between their ideas and their existence that took the shape of what the ancient Egyptians desired who were very creative and organized as each symbol had its own shape and meaning that came from their own lives. Each symbol played a role in their lives and often was related to ideas like life, death, birth, regeneration, power, love, protection, healing, weakness, hatred, and more. These symbols were referred to as the words of the gods and played a vital role in passing the culture and the beliefs of the ancient Egyptians from one generation to another.
Each one of the Egypt symbols was a reflection of the power and wisdom of the gods and played a role in their lives and often was related to ideas like Life, Death, Birth, Regeneration, Truth, Faith, Fertility, Power, Wealth, Luck, Happiness, Lust, Love, Protection, Healing, Weakness, Hatred, Peace and more.
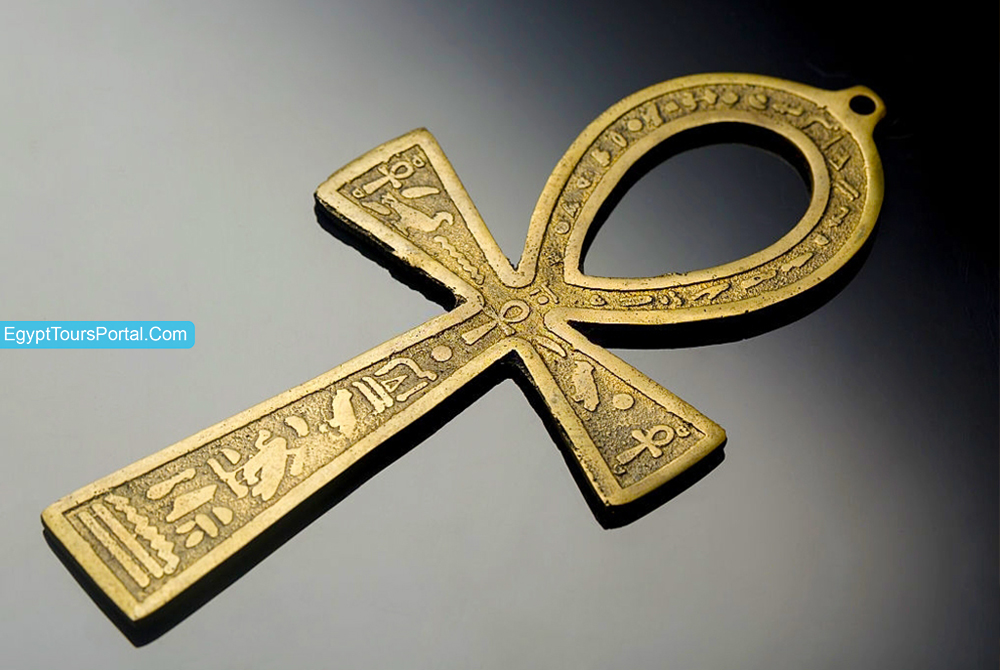

The Ankh is one of the most famous and used symbols of ancient Egypt and the world the Ankh showcases the concept of internal like and divine protection. It’s a cross with a looped top in a key-like shape, which has no beginning or end like the spirit of Ra, plus represents eternal life, the morning sun, purifying the life-giving power of water, clairvoyance, and the union of opposites like earth and heaven and male and female (Isis and Osiris). The Ankh symbol appeared in the Early Dynastic Period (3150 -2613 BCE) and by the Old Kingdom (2613-2181 BC) the Ankh symbol became a powerful symbol of eternal life and was known as Neb-Ankh. The symbol is associated with “The Knot of the Goddess Isis” and her powerful cult (c. 3150 – c. 2613 BCE) as it represents the bond that holds all of life together.
The Ankh symbol can be seen in the hands of mostly all the Pharaohs & the ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses. It’s also known as crux ansata by Coptic Christians which represents life and immortality. That symbol appears in paintings, on temple walls, and in tombs as it was the key to existence and used as an amulet to provide divine protection to the point where it was believed to be the key that can open the door to the afterlife. The Ankh can be viewed as a symbol of Joy and Balance between masculinity and feminity. The ancient Egyptian Symbol was referred to as the key of the Nile River which represents the eternal union of heaven and earth. The symbol of Ankh was often seen with the Djed and the Was Symbols.
Note: The Ankh symbol is a symbol for life, protection, faith, energy, transformation, light, and fertility. The Ankh can also refer to the concepts and symbols of sexual union between the two opposite sexes and fertility due to its connection to the goddess Isis. The Ankh is the clearest and simple example of the ancient Egyptian understanding of immortality, future life, reproduction, and overall the concept of the cycle of life.

The Djed is known as "The Backbone of Osiris", it represents strength and stability and is linked to the Osiris god of the underworld, and Ptah god of creation which makes it a symbol for resurrection and eternal life. Ancient Egyptians believed the Djed pillar was a combination of four pillars that held the four corners of the earth. It was also used as a fertility pole that rose during festivals which emphasized balance in life and hope in the afterlife, provided by the great Gods & Goddesses of Ancient Egypt. In the Old Kingdom of Egypt (2613-2181 BC), the ancient Egyptian symbol was featured on many temples, in the book of the dead in various versions, and used as an amulet.
A Djed column is often on the bottom of coffins where the backbone of the deceased would lay in order for the soul to stand up and walk into the afterlife. The raising of the Djed Pillar was viewed as the grains rising from the earth plus it also shows the soul rising up from the body and moving to the Afterlife. In the book of the dead, the Djed symbol is associated with directing the soul to leave the body and head towards the afterlife leaving the earth behind. A Djed column is often on the bottom of coffins where the backbone of the deceased would lay in order for the soul to stand up and walk into the afterlife.
Note: The spine of Osiris "Djed" is an ancient Egyptian symbol for stability in life and in the afterlife plus the enduring presence of the gods in one's life. It was an ancient Egyptian symbol for the Pharaohs, fertility, eternal life, triumph, balance, rebirth, regeneration, immutability, permanence, and abundant harvest plus the Djed symbol was viewed as a symbol of fertility and resurrection.
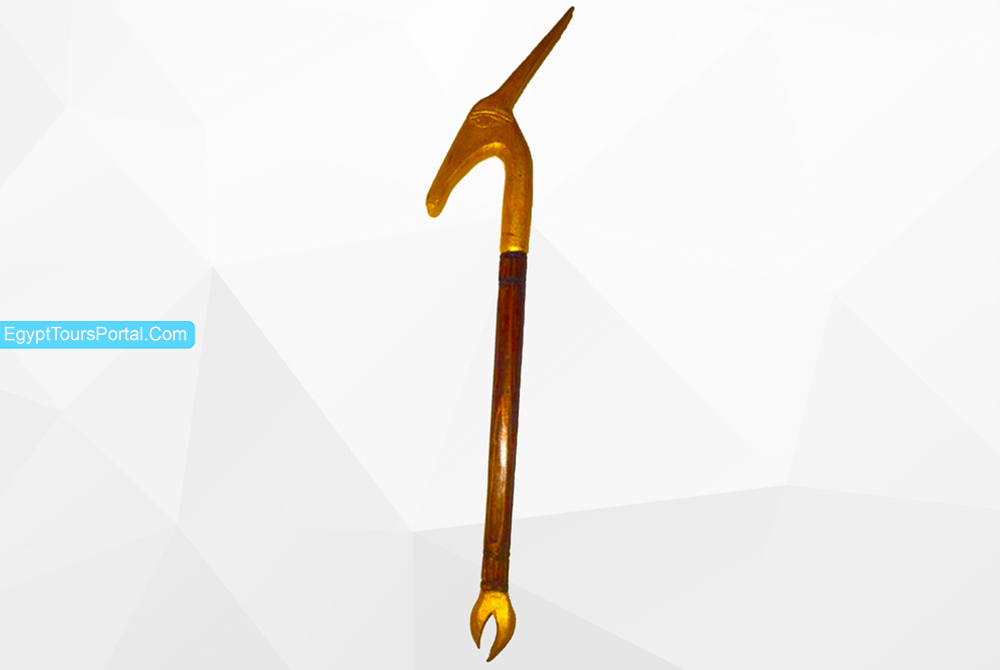

It was an ancient Egyptian symbol of power and dominion of the god and the king in ancient Egyptian history and culture. The ancient Egyptians believed the sky was supported on four pillars in the shape of a Was specter. It is known as “Sculptor of the Earth” which presented the absolute meaning of completeness and totality. The staff is topped with the head of a canine which was developed in the time of king Djet (c. 3000 – 2990 BCE) of the first dynasty. Each god had his own was specter-like Hathor, Isis, Ra, and many others.
The god Ptah was able to combine the Anka, Djed and the Was into his scepter, that was the only thing that fit his holiness. Since it was featured many times with set the god of chaos, the symbol was linked to the ideas of the desert, and war. The concept of the scepter would chance ideas depending on who was carrying the staff as in the hands of Isis; It represented duality and fertility, In the hands of Hathor; it represented happiness, In the hands of Horus; it symbolizes the sky, and in the hands of Ra; It symbolizes rebirth.
Note: The Was Scepter is an ancient Egyptian symbol for power, authority, dominion, plus wealth, and happiness. In the hands of Ptah, the Was scepter was combined with the Ankh and the Djed for the sculptor of the earth.

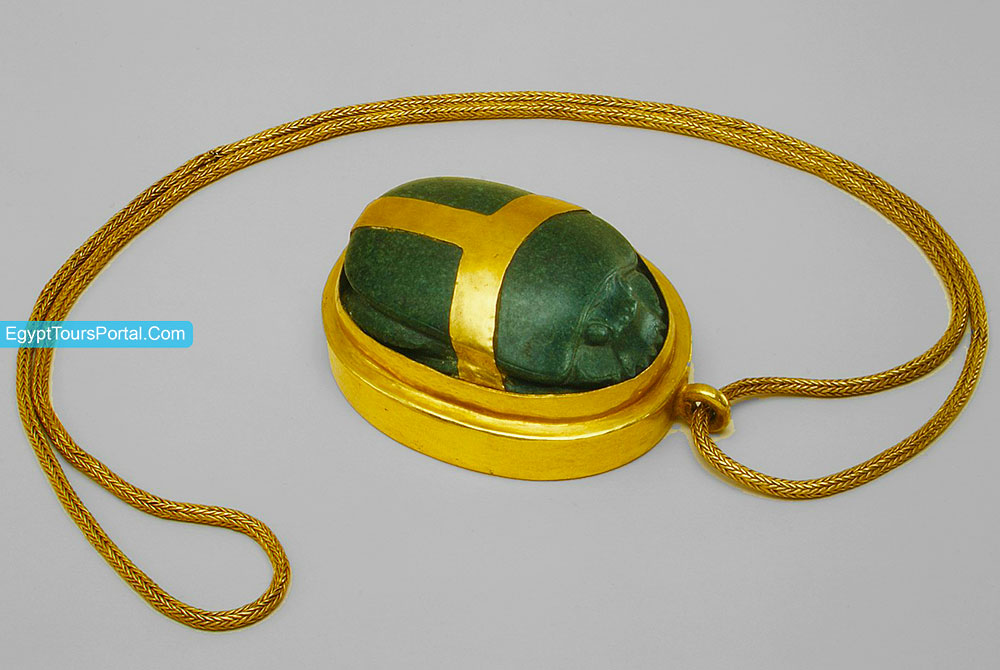
The Scarab symbol was one of the most well-known symbols of ancient Egypt during the first intermediate period (2181-2040 BCE) until the rise of Christianity. This ancient Egyptian symbol is seen in Egyptian art and iconography which is a species of the dung beetle. The shape of the scarab amulet came from the act of rolling the dung into a ball and laying its eggs in it and the dung served as food for the young when they hatched. Ancient Egyptians saw life coming from nothing which represented transformation, the recreation of life, and resurrection.
The scarab was identified with the God Khepri who was more like Ra’s assistant who rolls the ball of the sun across the sky. The scarab hieroglyph letter refers to the ideas of existence, transformation, growth, effectiveness, and divine manifestation which explain why the symbol was used in describing the titles of officials, governmental places, and creating official royal seals. The most common scarab amulets were the hardstone made from amethyst, green jasper, and carnelian.
Note: The Scarab is an ancient Egyptian symbol for life, death, good luck, transformation, growth, and creation. The Scarab was one of the most important amulets ever created in Egypt due to its power, influence, and importance in representing the ideal of immortality, metamorphosis, and the cycle of life.

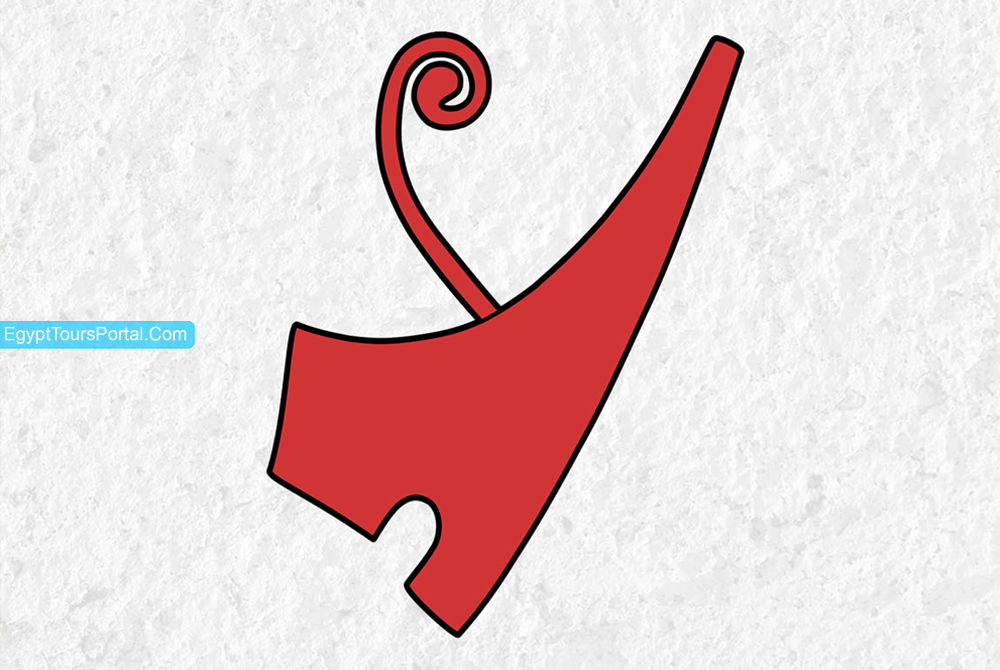
The ancient Egyptian Symbol Tyet Also known as Tjet, Tiet/Tyet, known as the knot of Isis or the blood of Isis, looks a lot like the Anka symbol except for its arms curved down. The symbol dates to the old Kingdom (2613 – 2181 BC) and represents the female genitalia. It was used as a funerary amulet made of a red stone or glass and was associated with many Ancient Egyptian Goddesses as well as Isis. It stands as a symbol for the female reproductive organs, and the goddess Isis in her role as the universal mother.
The Tyet was combined with the Djed to offer the complete union of the feminine power and the masculine power. The symbol was also linked to the Nephthys with the concepts of Burial and resurrection. It symbolizes the ideas of eternal life and resurrection. It is often paired with the Ankh offering the protection and security of both Isis and Osiris. In the New Kingdom of Egypt (1570 – 1050 BC) when Egypt reached its full glory and the cult of Isis reached its peak the symbol became very famous.
Note: The Tjet is an ancient Egyptian symbol for life, feminine power, security, protection, regeneration, love, blood & health. The symbol also reflects the concepts of Life and death as it represented the female sanitary during menstruation.

The lotus symbol is considered to be a true icon in Egyptian Mythology and ancient Egyptian art. The flower a.k.a “Water lily” closes at night, sinks underwater then wakes up in the morning, that’s why it became a symbol of the sun, creation, and regeneration. The Ancient Egyptian Symbol Lotus has been associated with Atum-Ra the sun god as a giant lotus emerging from the primordial waters of Nun when the world was born and from which the sun god appeared.
The cult of Osiris also used the symbol related to funeral imagery and with the deceased entering the underworld which symbolizes reincarnation. The symbol was commonly used in art to represent Upper Egypt. It was found in honored and sacred places all over Egypt, on the architecture of the capital tops of Egyptian pillars representing the tree of life, plus in the tombs, in Hieroglyphics, written in papyrus, found on thrones, and the headdresses of the divine pharaohs.
Note: The Lotus Flower is an ancient Egyptian symbol of Purity, cleanliness, Enlightenment, Rebirth, and Regeneration. This ancient Egyptian symbol of the sun reflects the concepts of rebirth and creation such as the flowers closing and sinking underwater in the night and then raising again the sunshine.

The Shen symbol is a circle of rope that has no beginning and no end, in order to form an unbroken bond which symbolizes infinity, completeness, eternity, and divine protection which made its symbol extremely popular and well–presented. The word "Shen" comes from the Ancient Egyptian word which means "Encircle", the amulet of Shen was worn by everyone including kings. It was often linked to the greek symbol omega which symbolizes infinity. Many deities like Horus and Isis are seen holding the Shen which made the ancient Egyptians honor the Shen as a symbol of symmetry and perfection as shown on countless personal objects, Temples, and Tombs.
Note: The Shen Ancient Egyptian Symbol of Royalty, Protection, eternity, and infinity. The Shen-Ring is associated with the sky falcon god Horus and used to encircle the sun and stands as a symbol of the eternity of the entire universe, Symmetry, and completeness.
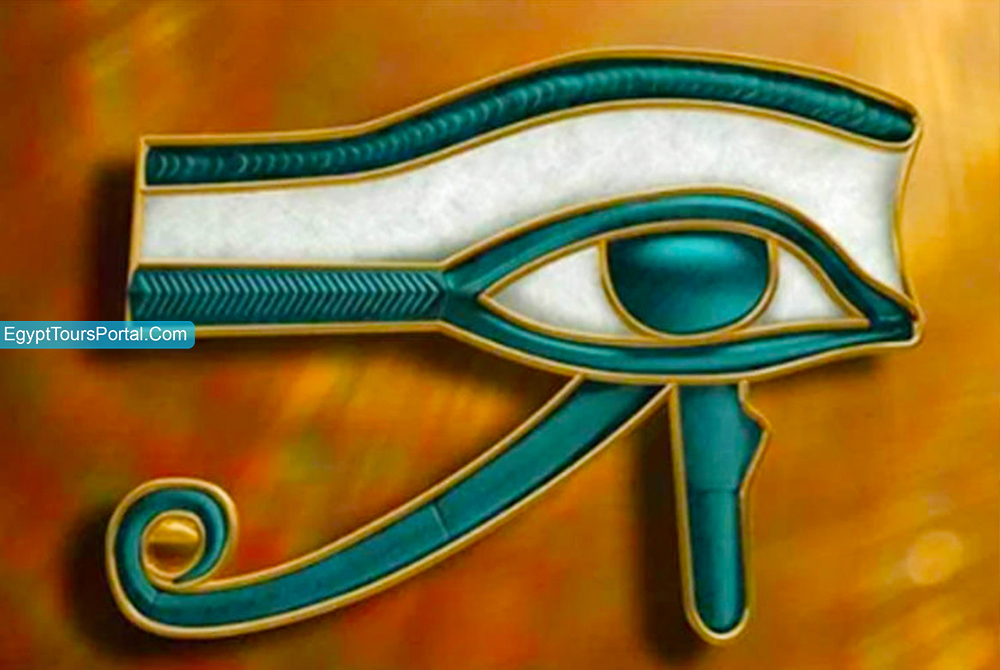

The ancient Egyptian symbol Eye of Horus is also known as (Uto, Udjat, Wedjat) which represents healing, protection, good health, good luck, Royal power, sacrifice, and curative qualities, and is the most famous of ancient Egyptian symbols. The left eye belonged to the sky god Horus who gave it away to save his father Osiris who became the ruler of the underworld, the eye was later restored after saving the life of his father. The left eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol that represents the magical abilities and powers of the sky which were either restored by Hathor or Thoth. This symbol is extremely famous and powerful at that time as it had healing powers and was used as a medical tool to measure the ingredients while making the medicine plus it was believed the eye of Horus had mathematical knowledge and power.
The eye of Horus is an incredible example of the mathematical knowledge of ancient Egyptian as the Eyes of Horus are divided into six parts and each part was given a fraction as a measurement unit. All the six-part of eyes is associated with different sense the right side of the eye represents smell, the pupil represents sight, the left side represents hearing, the curved tail that looks like a tongue represents taste, and the teardrop represents touch. The Amulets of the eye were made out of Gold, Lapis Lazuli & carnelian and found with both the dead and the living. The eye represents the moon and is considered a symbol of sacrifice. The Eye of Horus symbol corresponds to the location of the third Eye the key to clairvoyance. His right eye is known as the eye of Ra the sun god.
Note: The Wadjet "Eye of Horus" is an ancient Egyptian symbol for protection, sacrifice, healing, Royalty, knowledge, love, good luck, and power. The Eye of Horus "Wadjet" means the totality or unity restored referring to the myth of Osiris. It is a cross between a hawk's eye and a human eye plus it often comes in green to represent resurrection, vegetation, knowledge, and knowledge.

The Eye of the Ra is a famous ancient Egyptian symbol amulet capable of repelling all negative energy and creating total harmony. The origin of the symbol can be traced to a number of connected tales like the time when he sends his eye as a loving father to look for his lost children. During the absence of Ra’s original eye, another one grew. When the first eye successfully returned with the children, the eye was used as a weapon by other gods. The sun god Ra does his routine of sailing his boat across the sky during the day and then goes to the underworld at night when he was weak and vulnerable.
The myth says the daughter of Ra used the power of the eye to punish the humans who ignored his instructions and laws but many gods feared the eye would destroy mankind so they capture and calmed the eyes and then returned to Ra. The symbol represents royal power & authority, regeneration, and peace. The eye of Ra is associated with the destructive power of the sun, but the Egyptians also used it to protect buildings and themselves. The amulets were painted with a dark red color and worked to protect against evil entities or spells and create good health. Another representation of the eye of Ra is the symbol of a cobra wrapped around a solar disk.
Note: The Eye of Ra is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, love, good health, royal authority, and power. The Eye of Ra represents the power of the sun to provide protection and destructive force. The Eye of Ra is believed to repel all negative energy and establish balance & harmony and the power to see everything.
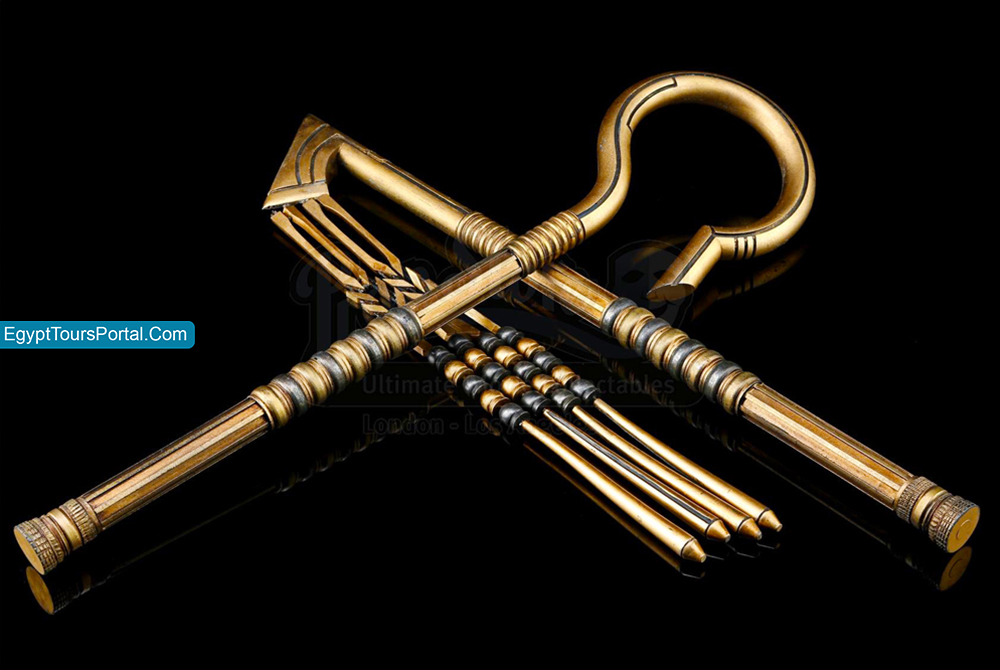

The Crook and the Flail were considered a symbol of the state’s power and the king’s absolute might and control over his subjects. The word “Hekha” is an epithet of Osiris which means “To Rule” and is considered a symbol of royal power and dominion. The symbols appear in the Early Dynastic Period during the reign of the first King Narmer (3150 BCE).
The crook and the flail were first used as two emblems of the god Osiris which symbolized the authority of the Pharaohs. The Staff represents kingship, the Pharaoh as the shepherd of his people while the flail stood for the fertility of the land and the Pharaoh as the provider of food for his subjects. It was made out of wood as the ancient Egyptians believed it was scarce but the kings always used ones made of decorated gold.
Note: The Heka and Nekhakha are ancient Egyptian symbols of kingship, power, royalty, fertility, the divine authority of the Pharaohs, and wisdom. The Crook represents the caring wisdom of the Pharaoh as the shepherd and the fail represents the scourge needed to maintain the order within the society. For these reasons, these symbols and artifacts have been found with the gods of pharaohs of Egypt across the ages.

Ouroboros is one of the ancient Egyptian symbols of the sun which represents the travels of Aton and one of the aspects of the sun god. It represents rebirth, perpetuity, and recreation plus showcases the beginning and end across time. The symbol was created when Atum came out of the dark primordial waters of Nun in the form of a serpent renewing itself every morning.
The symbol appeared for the first time in the tomb of King Tutankhamen when he was buried in the 14th century BC which showcases the unified Ra-Osiris. It is known as an infinity symbol, it’s used in many different cultures like in Greek and Norse mythology.
Note: The Ouroboros is an ancient Egyptian symbol of time, life, death, fertility, rebirth, good health, good luck, and the cycle of life. This symbol has appeared in Gnosticism and Hermeticism and most notably in alchemy in the shape of an emblematic serpent or a dragon that expresses the unity of all things both material and spiritual which changes form in an eternal cycle of total destruction and re-creation.

The Cartouche is one of the most ancient and classical symbols of the ancient Egyptian Civilization, it is a clear connection and powerful symbolism to the sun which showcases the divine protection against evil spirits within this life and the afterlife. In Hieroglyph the cartouche represents the Egyptian-Language word for Name. It is an oval with a line at one end at right angles oval with a horizontal bar with a royal name in the middle. They were written on tombs and coffins to show who was located inside to help the body find its way across the Afterlife.
Note: The Cartouche is an ancient Egyptian symbol of good luck, and protection from Evil in life before and after death that's why it can be found located in tombs. The symbol is believed to be an expanded version of the shen-ring.

The Uraeus is an ancient symbol that represents the cobra the animal representation of the goddess Wadjet of royalty. The symbol is the embodiment of sovereignty, royalty, and divine authority. The ancient Egyptians believed that the Uranus symbol can provide magical powers and protection according to the myth of the cobra that was given to the pharaohs from the god Geb of the earth as a sign of kingship. The Uraeus was used as an ornament for statuary, was found on the top of his crown, and as an adornment on the pharaoh plus for jewelry and in amulets. It was also used in hieroglyph that represents a shrine or a building.
Note: The Uranus is an ancient Egyptian symbol of royalty, the Sun, sovereignty, protection, divinity, and authority. It describes the legitimacy of the pharaoh and declares him the Great of Magic. It is a Royal Symbol that has been featured with many gods across the ages, it was referred to as the Eye of the moon, the Eye of Hathor, the Eye of Horus, and the Eye of Ra plus it was shown with many pharaohs such as King Tutankamun.
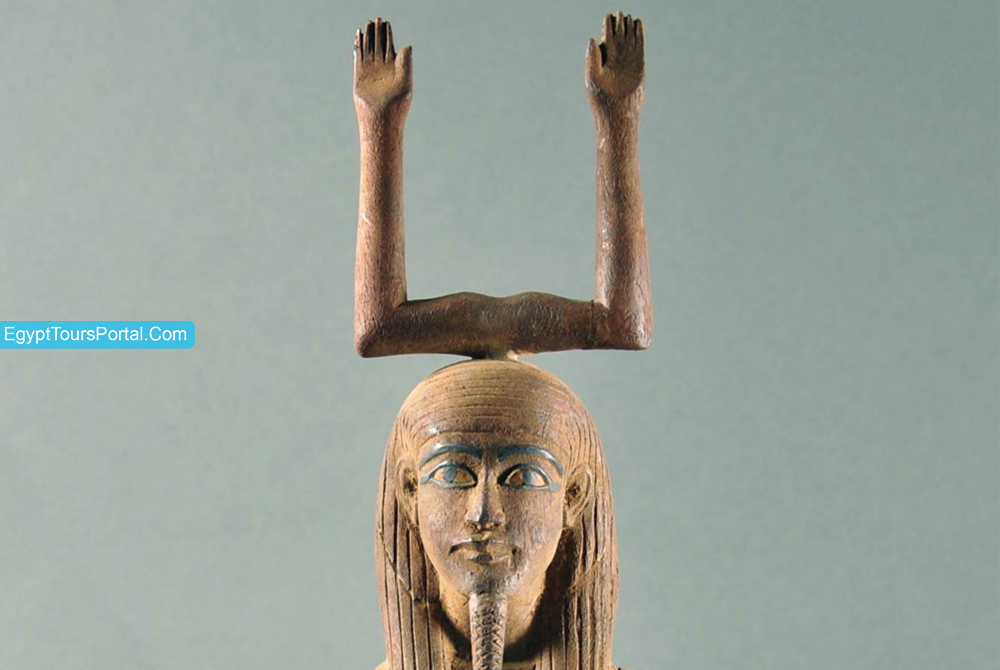

The ancient Egyptian symbol of the ka means spirit and soul as it was believed to represent the souls of the newly born and resurrected in the afterlife. The Ka is the life force and the spiritual essence of the soul and the most complicated part in ancient Egyptian symbolism and mythology which was viewed as the gateway to the heavens that affects every single aspect of their lives. The Ka was the reception of the life powers of each man from the holy gods. It was also the source of these powers and the spiritual double that resides with every man plus the ultimate symbol for the sustaining and creative power of life. The Ka was part of the soul which was a person's double that lives inside his body until death.
After a person died the spiritual aspect of every human being will be the body but it needs to return back so that's why the ancient Egyptians mummified to maintain it as long as possible so they could win their chance to enjoy eternal life. Kas of royalty represented individuality while that of the common people are usually related. Divine Kas were believed to be guardians as the Ka of Osiris was believed to be the sentinel of the pyramids and The Ka is often seen with the Horus-name of the king on the pole. The ancient Egyptians viewed the Ka as the conscience or guide of each person plus kindness, honor, compassion, and quietude. The hieroglyph for the ka was the shoulder and arms bent upwards at the elbow. The Ka statues and images are depicted in an idealized state of vigor, youth, and beauty. The Egyptians believed that all mankind was made from clay by the ram-headed god named Khnum.
Note: The Ka Symbol is an ancient Egyptian symbol of soul, spirit, life, death, rebirth, afterlife, youth, vigor, and eternity. The Ka is simply the life force or soul given from the gods to mankind but it still remains independently from the person as the conscience that could lead a person to the path of righteousness.

The ancient Egyptians believed that the passage to the afterlife equaled the weight of a feather. One of the most recognized and famous ancient Egyptian symbols is the feather of Ma'at which was one of the forms of the goddess Ma'at who represented the ancient Egyptians concepts of order, harmony, law, balance, morality, truth, and justice. The Process of Judgment in the Afterlife was heavily dependent on the feather of Maat.
When the body of the deceased was delivered by Anubis to the hall of Truth to stand in front of the ruler of the underworld Osiris then the judgment begins by weighing the feather of Ma'at against the heart of the deceased and the weightlessness of the heart. If the weight of the deceased heart is lighter than the feather then the person enters the eternal land of the field of the reeds but if the heart of the deceased was heavier than the feather of Ma'at then he would be devoured by Ammit a soul-eating monster that makes you vanish from existence.
Note: The feather of Ma'at is an ancient Egyptian symbol of justice, truth, order, balance, and the law. The symbol was seen as the motto of cosmic balance between the power of good and evil, life and death. The feather played a vital role in deciding the fate of each soul at the weighing of the heart in the hall of truth in Duat. The Egyptian Pharaohs were depicted with the symbol of Maat which emphasizes their job of upholding the laws of righteousness.
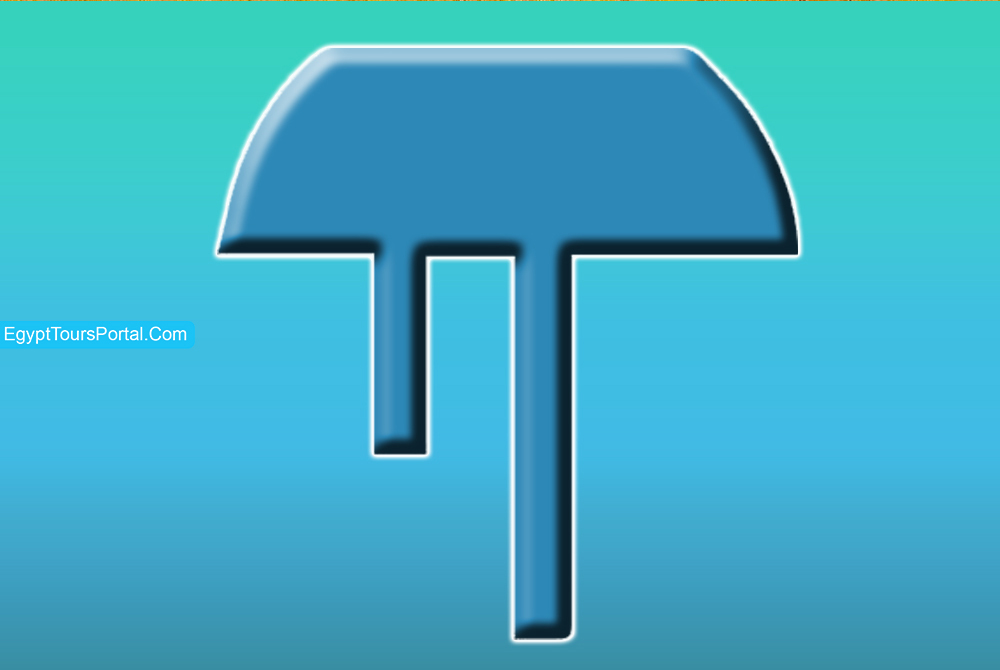

One of the most unique symbols in ancient Egypt is the Amenta which represents the land of the dead and the underground also known as Duat. The symbol was originally created to represent the horizon where the sun sets and a representation of the Nile's west bank which was the place where the ancient Egyptian buried their dead.
Note: The Amenta represents is an ancient Egyptian symbol of the underworld, the land of the dead, and showcases the horizon where the sun sets plus it represented the Nile's west bank where the ancient Egyptians buried their dead.
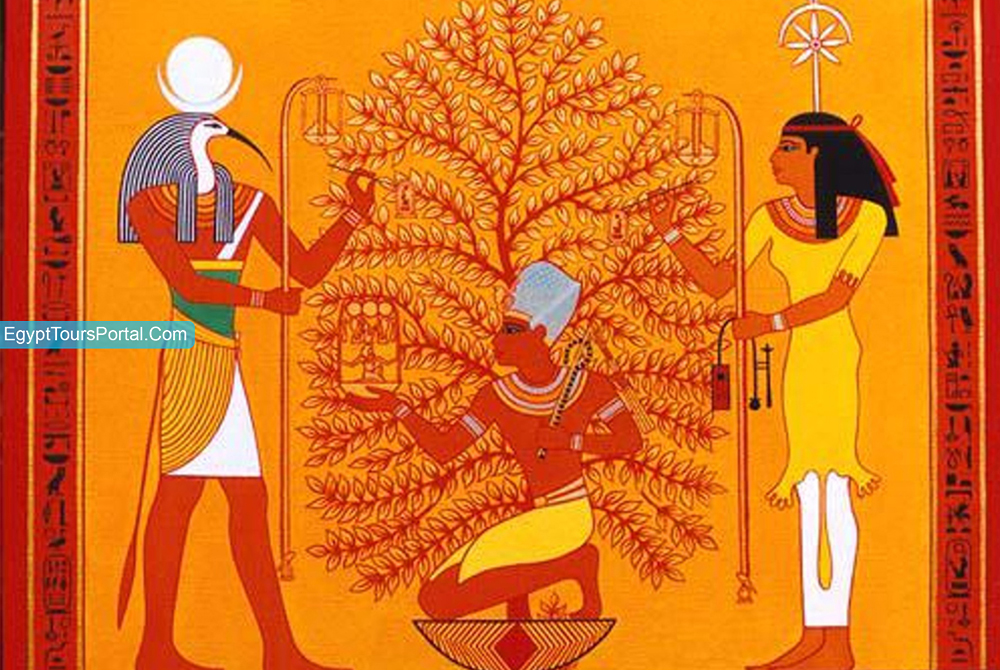

Every ancient civilization across the world has had its own version of the tree of life which was linked to the strong presence of water. All across Egypt, the three of life was an ancient Egyptian symbol that has a deep effect on their way of mythology. Many Egyptians believed that the three provided eternal life and full knowledge of the cycles of time.
The symbol of the tree of life was connected to the sun and believed it has the shape of a palm and sycamore tree which was believed to grow at the gates of heaven. It is connected with the creation myth and the nine gods of the Ennead of Heliopolis. The first appearance of the tree of life was in Heliopolis at the temple of the sun god Ra. The tree of life also known as the sacred Ished tree was the seat of the Bennu bird a.k.a the phoenix and was connected with the Djed symbol.
Note: The tree of life "The Sacred Ished Tree of Life" is an ancient Egyptian symbol for eternal life, regeneration, and knowledge of the divine plan or the equivalent to a map of destiny. It is an icon featured a lot in the mythology of Egypt, the fruit of the life tree is able to provide eternal life and the knowledge of the cycles of time, destiny, and the divine plan of the gods. The fruit was only available for the pharaohs and not the common mortals.

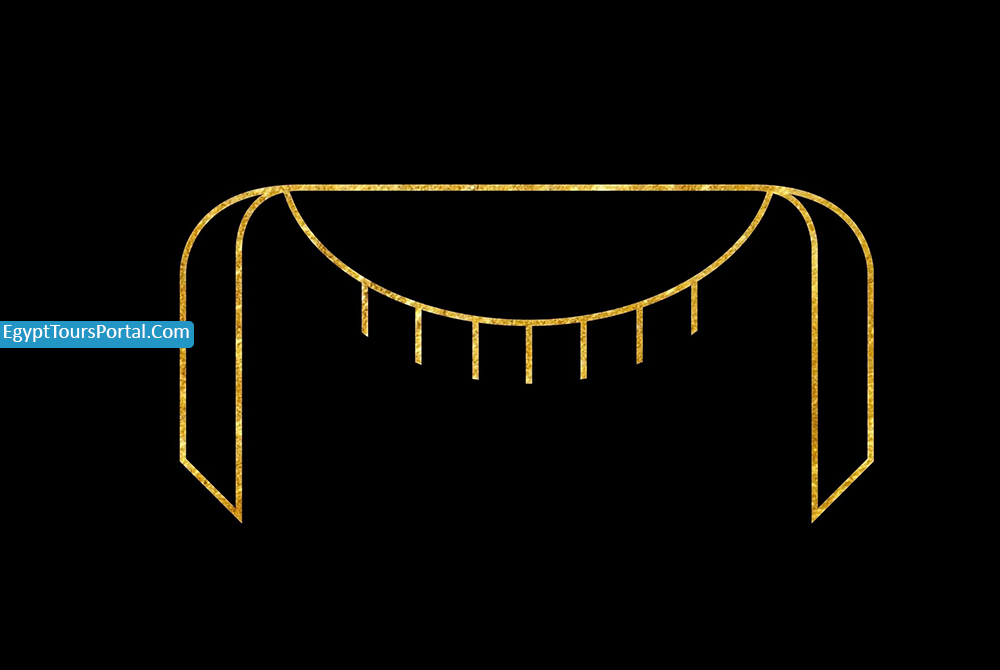
The Menet symbol is a strong religious symbol that comes in the shape of a necklace with a characteristic shape and counterweight. The Name Menet was also the name of the goddess Hathor of love, joy, and celebration. The ancient Egyptian symbol came in the shape of a necklace that was connected to Hathor & Apis Bulls as a protective amulet.
The Menet was shown as a symbol of birth, life, fertility, and regeneration. The Necklace was very popular in the new kingdom as it brought good & fortune and provides divine protection against evil spirits in this life & the afterlife and was used as a conduit for passing the power of Hathor to all her followers.
Note: Menet Is an Ancient Egyptian Symbol of Fertility, Life, Birth, Good Health, Rebirth, Renewal, Potency, and the Afterlife. The Symbol was in the shape of a necklace found on many goddesses and found only in the elite of ancient Egyptian society. During the festival of Hathor, her priestesses will shake the Menat and the sistrum in each household which symbolizes the coming of good health and a life of fortune.
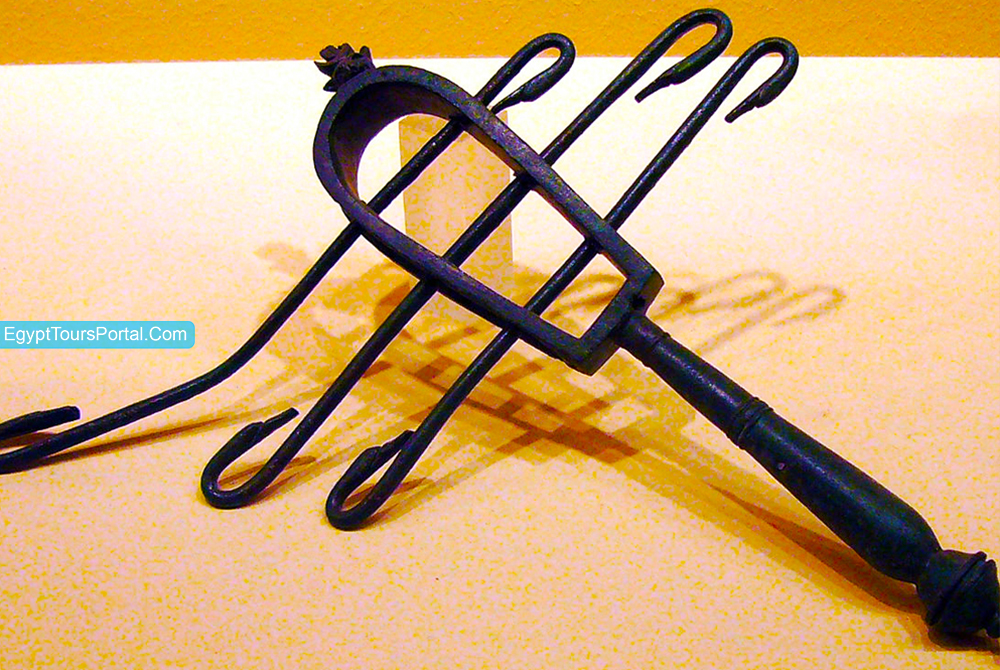
The ancient Egyptians were very creative in every aspect of their lives including music as they constructed musical instruments such as the sistrum which consists of a handle and a U-shaped metal frame made of bronze or brass, between 30 to 70 cm in width, plus it carried small moveable rings that produced a sound. It was used as an important instrument in the Egyptian cosmogony in religious ceremonies in the worship of Hathor plus the shaken it was to avoid the flooding of the Nile. Isis the goddess of motherhood and Bast the cat goddess of protection was also featured with a sistrum.
Note: The Sistrum is an ancient Egyptian symbol of music, good luck, good fortune, good health, joy, life, festival, dance, and eroticism. It was believed that this sound appeases and attracts the attention of the gods and goddesses so it was used to reduce the devastating effects of the flooding of the Nile.
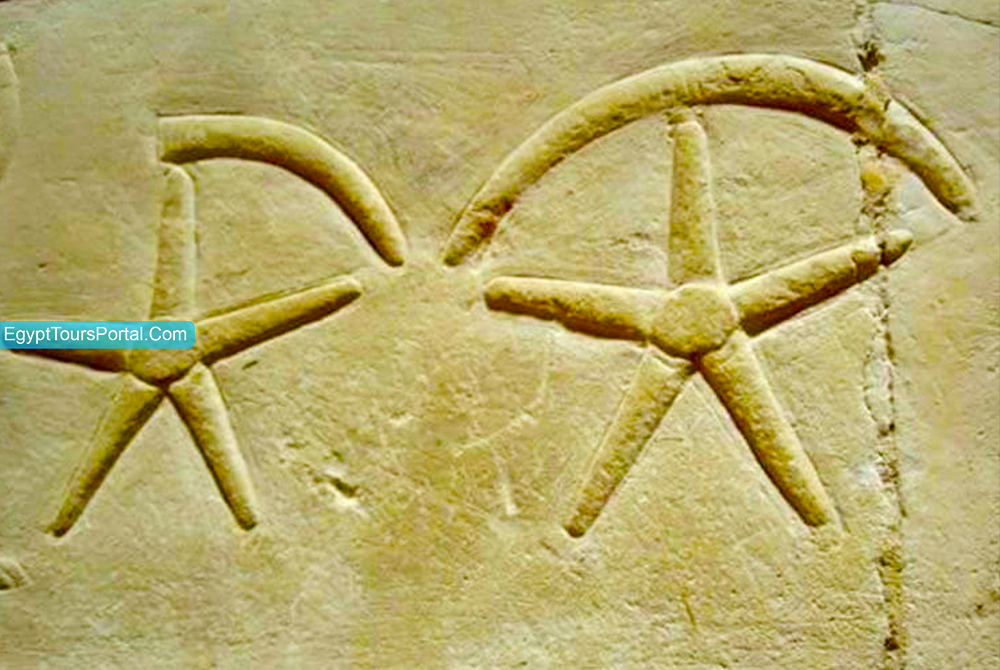

The Star amulet also known as Seba is an ancient Egyptian symbol that represents the stars which had a deep effect on architectural elements as it was used to decorate a number of temples and tombs plus their advances in astrology developed their calendar and their beliefs in the afterlife. The word Seba means ‘learning’ or ‘discipline’ and is associated with doorways and gates.
The symbol is associated with gates and doorways and the concepts of learning and discipline. The Egyptians believed that the stars represent the souls of the dead and the followers of Osiris. The Egyptian sky goddess, Nut is also shown adorned with five-pointed stars. The stars had a great deal of influence on the development of their calendar which was dictated to their beliefs in life after death.
Note: The Seba is an ancient Egyptian symbol of the stars, religion, time, afterlife, the Duat, the star-gods, and constellations. It is connected to the ideas of new beginnings, learning, traveling, guidance, and discipline.

One of the most famous ancient creatures and symbols in ancient Egyptian mythology and religion is the Bennu bird which is also known as the Phoenix. The bird represents the concept of resurrection and the rising sun. The Bennus was known to represent the soul of Ra the sun god and took the city of Heliopolis as the headquarter.
The tree of life also known as the sacred Ished tree in the city of Ra Heliopolis was the seat of the Bennu bird. The Bennu Phoenix was also linked with the inundation of the Nile and the ancient Egyptian concept of creation. The Bennu was seen as a lord of the royal jubilee which is a form of resurrection and rebirth like the sun. The name of the Bird is derived from the word "Weben" which means "to rise" or "to shine".
Note: The Bennu Bird is an ancient Egyptian symbol of rebirth, regeneration, life, power, and healing. The Bennu phoenix is a sacred bird in Heliopolis and is the Ba of the sun god, Ra.

The most spiritual and religious item in ancient Egyptian mythology is the canopic jar that played a vital role in the process of mummification, resurrection, and judgment. The ancient Egyptian believed that life was immortal and death was a door to the other side. The ancient Egyptians have four jars that were used to hold organs like intestines, lungs, stomach, and liver after being removed from the body, embalmed, anointed then wrapped in linen.
The heart that remained inside the body contained the soul. The jars were placed inside a canopic chest and then buried inside the Egyptian Tombs with the sarcophagus of the deceased. They were carved from limestone or pottery and used from the old kingdom till the Ptolemaic period. The heads of the jars wear carved to resemble the "Four Sons of Horus" who were also considered the cardinal compass points; the baboon-headed Happy, the jackal-headed Duamutef, the human-headed Imsety, and the falcon-headed Qebehsenuef.
Note: The Canopic Jar is an ancient Egyptian symbol of immortality, burial, afterlife, Mummification, transformation, and Protection. Every Canopic Jar represented all of the four sons of Hours to provide the ultimate protection.

The goddess of motherhood, healing, magic, and fertility Isis was the inspiration behind a number of symbols and amulets such as the Crescent moon symbol which is believed to bring good fortune to all mothers and their children.
Note: The Crescent is an ancient Egyptian Symbol of the lunar power of the moon, Fertility, Motherhood, Rebirth, and the Birth cycle. The crescent moon symbol is known as the sun shining at night, the eye of Hours, and can be found with the god Khonsu.
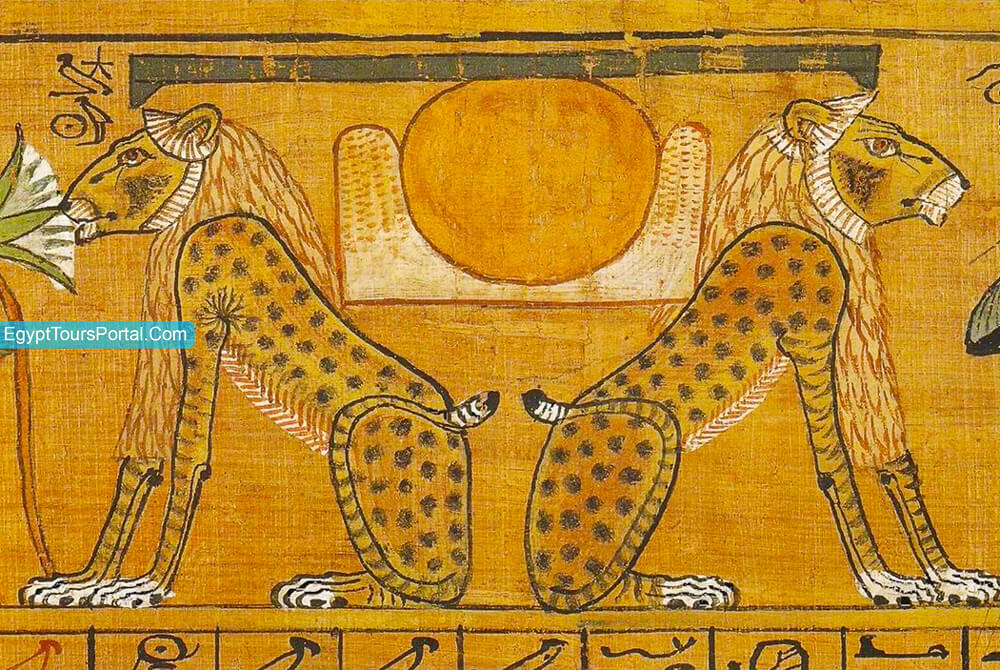

The Ajet is an ancient Egyptian symbol that was used in the writing of hieroglyphs which meant representation of the horizon and the sun. The Ajet represents the natural phenomenon of sunrise and sunset plus the concepts of creation and rebirth. The symbol means the horizon or the mountain of light. The circle in the middle of the center represents the sun and the figures found at the base are mountains. The symbol is protected by the god of the underworld Aker who comes in the shape of two lions on each side, each one representing the eastern and western horizons of the Egyptian underworld and also yesterday & today.
Note: The Ajet is an ancient Egyptian symbol of sunrise and sunset, and a Hieroglyph showcasing the power of the horizon, and the full power of the sun. The symbol represents the concepts of creation and rebirth & the past and the present.
The Headdress was a crown worn by the ancient Egyptian kings and queens to identify them as the official rulers. They show authority and took part in religious ceremonies and festivals as shown at the Temple of Abydos. The crowns were also worn by a number of deities as well to showcase a certain significance and symbolic meaning. The crown wears made of soft and delicate materials made from fabric, leather, or woven fibers like papyrus. Some of the most important crowns are:
It was worn by the rulers of Lower Egypt located in the north of Egypt around the Nile delta. The crown is worn by a number of gods and goddesses that showcase the role of the rulers who were blessed with the divinity of the gods themselves. Found on the forehead of the kings on the crowns is a Uranus dedicated to the cobra goddess Wadjet the protector of lower Egypt.
Note: The Deshret is an ancient Egyptian symbol of fertility, fortune, power, and royalty. When combined with the Hedjet the White crown of Upper Egypt, the resulting crown is the Pschent which symbolized the unification of the country.

It was worn by the kings of Upper Egypt and gods like Osiriswho lived in southern Egypt south of Memphis city all the way near modern Aswan. It is believed to have been first used between 3500 and 3200 BC proceeding the dynastic period in Egypt. The Crown was protected by the vulture goddess Nekhnet protector of Egypt shown on the forehead of kings on the crown.
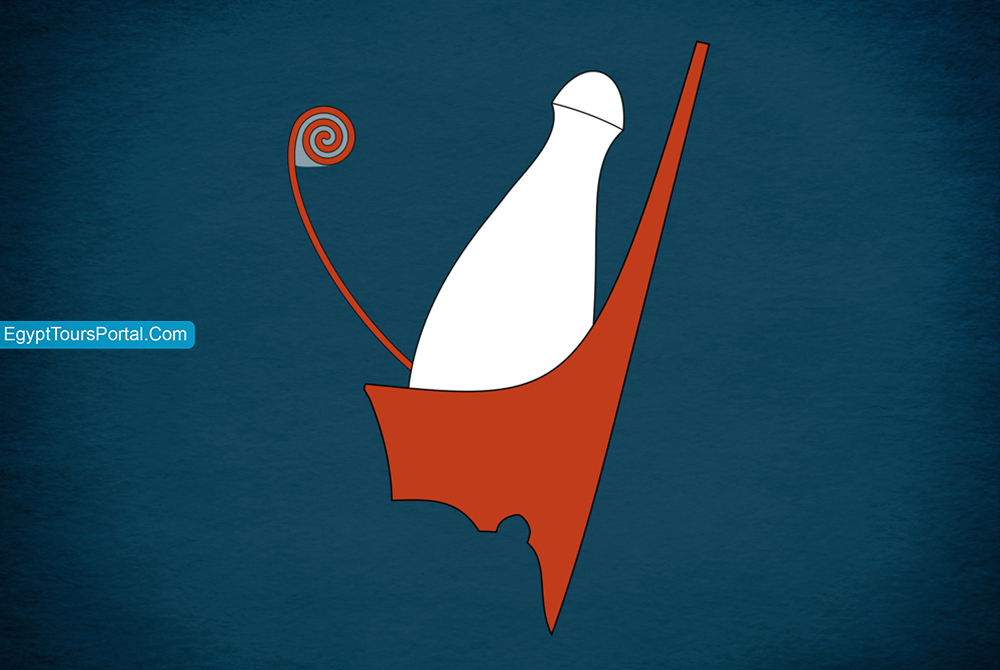

It is a mixture of the Deshret and the Hedjet that symbolizes the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under a single ruler. Horus was seen featured with his crown all the time and Menes was the first Pharaoh to ever wear it.
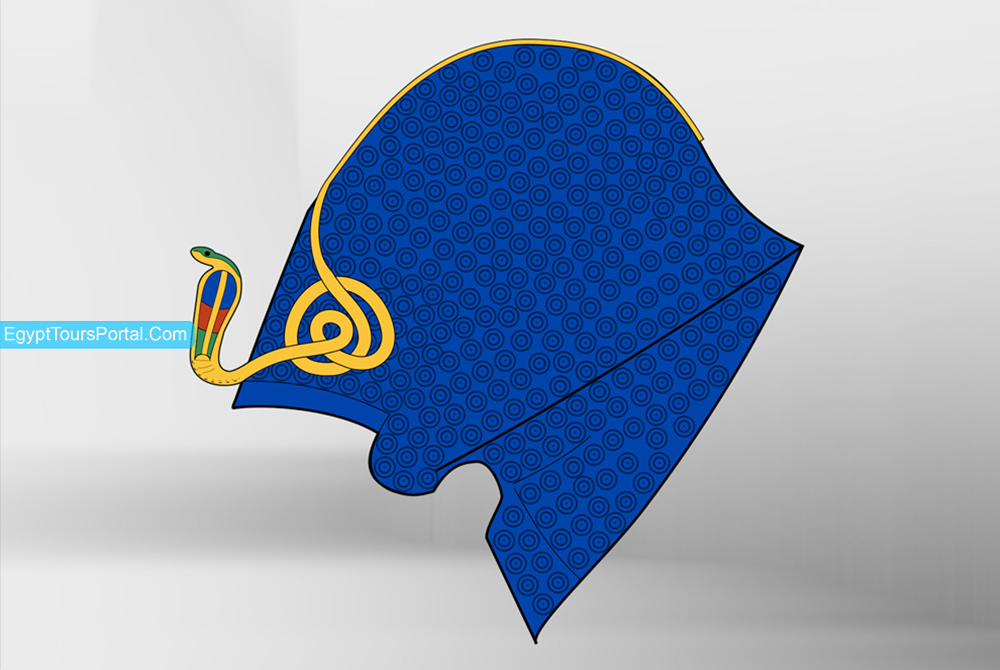

It is also known as the war crown as it was worn by kings of the 18th dynasty of the new kingdom who used to wear it at the time of battles. Ramses the Great was seen many times across his temples like Abydos wearing the crown.
Note: Khepresh is an ancient Egyptian symbol for the royal insignia and regalia which is associated with the Pharaoh. It represents the sky and the divine power of the Pharaohs & gods.

The Nemes is not really an ahead crown but rather a striped fabric headcloth reaching the shoulders worn by the rulers of ancient Egypt such as the boy King Tutankhamun who is seen wearing one on his golden mask.
Note: The Newes is an ancient Egyptian symbol of ancient Egyptian regalia, rebirth, royalty, Pharaohs, power, and authority. It represents the Royal Ka and can be seen on the head of all the deities and Pharaohs across history.

One of the oldest ancient Egyptian symbols is the Egyptian winged sun which dates all the way back to the old kingdom to showcase the concepts of divinity, royalty, and power. The symbol known also as Bendety was featured across a number of temples to represent the god of the midday sun Behedti which was connected to the sun god Ra and Horus. It is used as an amulet to provide protection. The symbol can be seen a lot flanked by the Uraeus on both sides.
Note: The Winged Sun is an ancient Egyptian symbol of divinity, royalty, power, protection, and eternity. The concept of the winged solar disc existed since prehistoric times in the form of a falcon spreading its wings then a solar disc was added. It became a symbol of the solar and the heavens and represented an aspect of Horus the protector of the kingship and the personification of the divine ruler of the whole of Egypt.
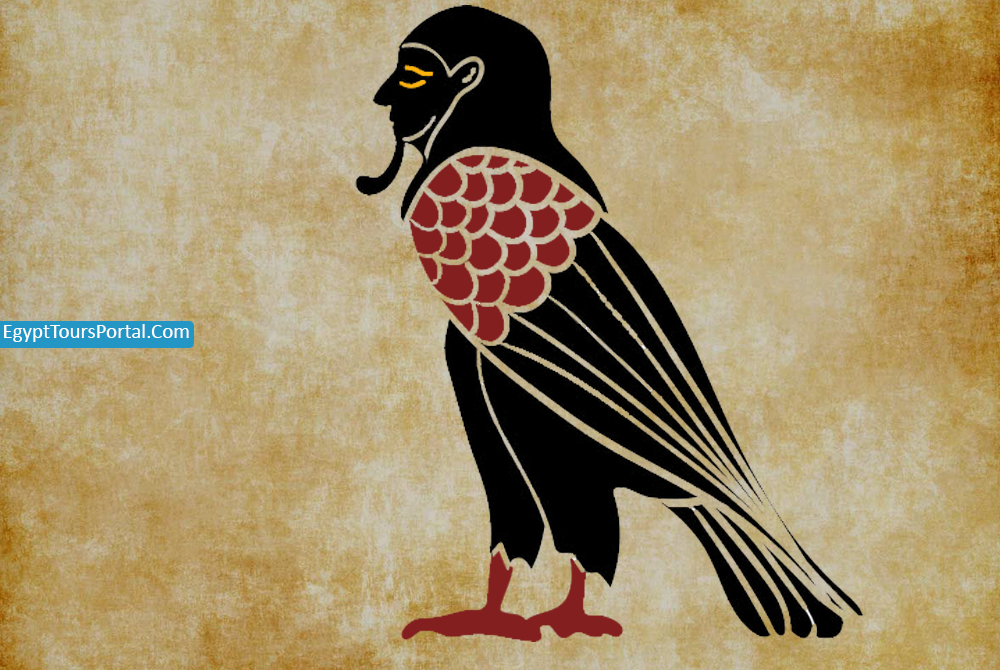

The Ba is an ancient Egyptian symbol of the personality, the spiritual manifestation that leaves the body at the point the Death which is an integral part of the individuality of every human being. It is showcased as a falcon or a bird with the head of a human. The Ba is is the roaming physical essence of the soul and the emblem of the soul ascension after death. Some believe that Ba influenced the creation of the Mummification process so the Ba spirit can return to the body at night. The Ba has the power to tow the Barque of the sun and travel every night in the underworld.
Note: Ba is an Ancient Egyptian Symbol of the soul, rebirth, divinity, death, life, and afterlife. It is the roaming Physical essence of the soul. In the ancient Egyptian Religion, the Bas was seen as a bird with a human head that would unite with the Ka and bring the mummy to life.
The Nebu Is an ancient Egyptian symbol of Gold which was considered to be a divine metal from the heavens that was believed to be the flesh of the gods. It is connected to the sun god Ra who is known to be the Mountain of Gold. Its polished surface is linked to the brilliance of the sun and in the afterlife, it represented aspects of immortality. In the old kingdom, the pharaohs were known as the golden Horus and in the new kingdom, the royal burial chamber of the Pharaohs was called "The House of Gold".

The Djew is an ancient Egyptian symbol of the afterlife, tombs, death, and Royalty. The ancient Egyptians believed that the heavens were held by a cosmic mountain which two peaks with the Nile River in the middle which would explain the tombs were located across the mountainous lands bordering the Nile valley. Anubis the god of the dead was referred to as "He Who is Upon His Mountain".
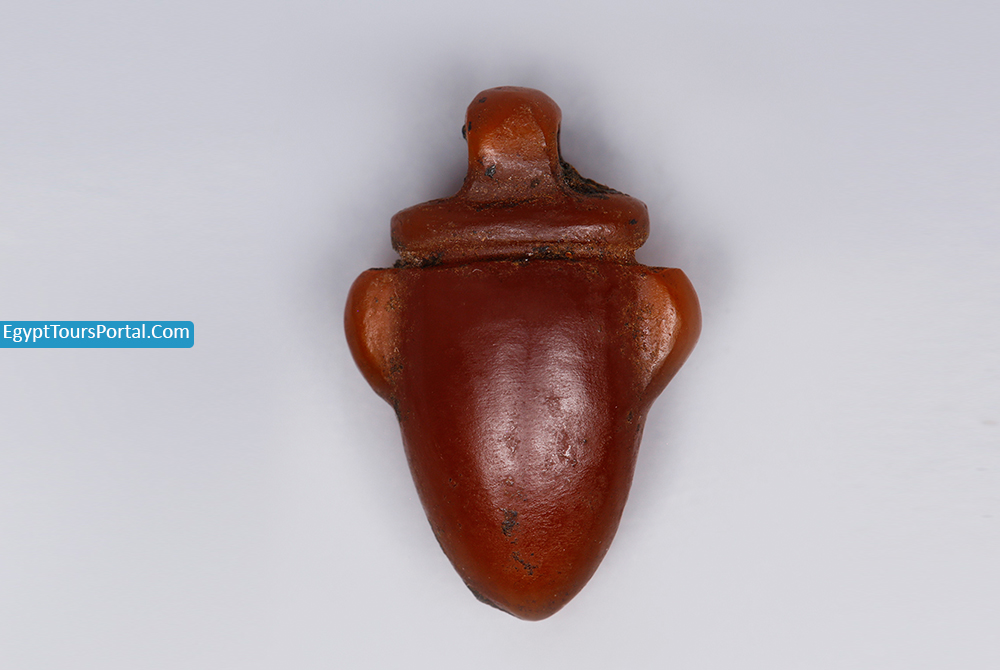

The Leb is an ancient Egyptian symbol of the heart which was believed to be the center of all consciousness and even the center of life. It was the only organ not removed from the body.
The PrimordialHill Is an ancient Egyptian symbol the ancient Egyptian believed in the moment of creation of a hill from the water of darkness and created drylands which inspired the ancient Egyptians to make these incredible immortal constructions.

The religious Egyptian Symbol of the Heart (IB) can be seen as the Key to entering the afterlife as it was a vital part of the judicial process in front of Osiris in the hall of Truth through the weighing of the heart ceremony where the heart was examined by Anubis then put on a scale against the feather of maat to ensure the owner of the heart has been able to find balance throughout his or her life. It was seen as the metaphysical embodiment of memory, intellect, and wisdom plus emotions like love, bravery, and sadness. It was placed and storied in the mummified body and secured with the heart of a scarab to prevent the heart from telling any tales.
Note: The Symbol of the IB is a symbol of the physical heart that was needed to perform and finalize the fate of each human. It is a symbol of intelligence, thought, memory, wisdom, sadness, bravery, and love.

The Physical form where the souls existed Khet was necessary in order for the soul to possess intelligence as it stands in front of the guardians of the underworld. All the bodies were mummified and stored in their own burial chamber which the life of the deceased decorated across its walls so everyone can remember their past. When the judgment ceremony took place, the body was awakened by a series of funerary rituals and rites to unite with its soul once more. The quality of the body has an effective impact on the quality of the afterlife that’s why the ancient Egyptians seeks to improve the mummification process to perfection plus provide the deceased with the finest tomb in order to maintain the viability of his Khet.
Note: The Khet symbol was the physical manifestation of the soul and house where the soul acted and survived until the time of judgment.

The Ancient Egyptians believed that the Akh belongs to the sky, and the Ba/Ka belongs body of the earth. The AKH is a magical concept associated with thought and intellect as a living entity that has changed many times across the vast history of ancient Egyptian and was described as some sort of a ghost. The best way to describe the Akh is a spirit with unfinished business who chooses to revisit the world by taking any form they desire. The Akh was created when the Ka and the Ba reunited once again It had the power to do good or harm to the person’s wellbeing, the power to cause nightmares, sickness, and feelings of guilt, and also can be used to assist living family members
Note: The Akh was often identified with the power of light and conviction as a living identity that can still affect reality.

The Obelisk is a powerful and famous ancient Egyptian Symbol that represents creations, rebirth, unity, kingship, power, and achievement. The obelisk stands as an example of the concept of duality and balance. It is the most popular construction monument ever created that symbolizes Ra the sun god plus it was seen as the petrified ray of the Sundisk Aten. The divine Benben came from the primordial waters of NU where Atum created the universe which had the shape of an obelisk. It is associated heavily with the astronomical phenomena related to sunset and sunrise plus sun pillars and zodiacal light.
Note: The Obelisk and Pyramid Symbols are symbols of the living deity, the vitality and immortality of the pharaoh, and the divine power that lead to the creation of the greatest civilization on the face of the earth.

The Reed or Su Plant and the Bee are magical symbols that represent the union of Upper and Lower Egypt "The Two Lands". The Word Nesw which means the reed stands as a symbol for Upper Egypt plus "Bit" which is a bee that stands as a symbol of Lower Egypt; when they are put together, they become a symbol of the powerful domain of the Pharaoh as the eternal ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt.
Note: The Bee and Reed Symbol represents the unity of Egypt and the tradition of honey keeping during ancient Egypt.

The sacred water plant of the Papyrus stands as a symbol of the primeval marches of creation and for the power of writing and knowledge. It was also used as a political symbol for the delta of Lower Egypt plus the Unification of both Upper and Lower Egypt. It was heavily connected with the god Thoth of writing, wisdom, and knowledge. It was always seen changing its power and divinity from the river banks of the Nile.
Note: The Papyrus is a majestic symbol showcasing the power of knowledge and writing plus the artistic evolution of ancient Egypt.

The exotic Vulture symbol of Upper Egypt was seen as an insignia for royal protection provided by the goddess Nekhbet. It can be seen appearing next to the Uraeus on the headdress of the kings plus seen clutching a Shen by her claws thus representing eternal protection.
Note: The Vulture symbol is an enchanting symbol of divine protection from one of the oldest ancient Egyptian gods in the history of Kingship.

The rare Egyptian pool represents Water, especially the primal waters of Nun which is the main source of all things, plus many sun gods of ancient Egypt are seen dedicated as the sun itself rising from the pool symbol. It is depicted as a rectangle, long horizontally with equal seven spaced vertical wavy lines. The image of the pool symbol can be seen across many tombs and temples where a fruit-laden palm tree is grown and the Four Sons of Horus are rising from a lotus flower emerging from the side of the pool.
Note: The Egyptian pool is a blessed symbol of the divine power of the water that created life in the middle of the harshest environments on earth.

One of the oldest symbolic religious objects in Egypt is the Imiut fetish which is a stuffed animal skin tied to a pole in a lotus bud and put as a stand. It is one of the oldest ancient Egyptian funerary rites dating all the way back to the First Dynasty (3100–2890 BC). It was referred to as the Anubis fetish and was associated with the mummification process.
Note: The Imiut fetish is a unique symbol showcasing the rare and exotic religious funerary rituals of ancient Egypt.

The Hennu symbol represents the symbol of the falcon god Seker of Memphis. Ra used a vessel in the day called the Mandjet and in the night was the Mesektet. The Hennu boat and Sokar barque were used and sailed by Ra to being light to the world while being assisted by Seker who had a deep connection as the triple god of Ptah-Seker-Osiris.
Note: The Solar boat symbol represents the sacred journey that every soul will have to take to make it across to the afterlife.

The magical Sema symbol is an ancient concept that always existed in the minds of the ancient Egyptians as it represented the concept of Union. It is found depicted across the magical Upper and Lower lands of Egypt. The ancient Egyptian saw the Sema symbol in everything like the pair of lungs being attached to the windpipe to breathe and the different genitalia of both genders coming together to create life. The Sema symbol was located in ancient Egypt on the mummy’s chest to provide life while traveling across the underworld.
Note: The Sema is a meaningful symbol that showcases the importance of the concept of Union to the ancient Egyptians.

The ancient Egyptian symbol Sa represents protection, especially for a young life, which is very connected with the god of fun Bes and the Hippopotamus goddess Taweret protector of women during childbirth. It is connected to pregnant women and to mothers who wish to protect their kids from evil. It has the shape of a loop that was used as an amulet that offered a magical bond of protection between this mortal world and the supernatural one.
Note: The Symbol Sa was dedicated to the protection of women during childbirth by the goddess Taweret which only showcases the vital role the ancient Egyptian women played in further building the Egyptian empire.
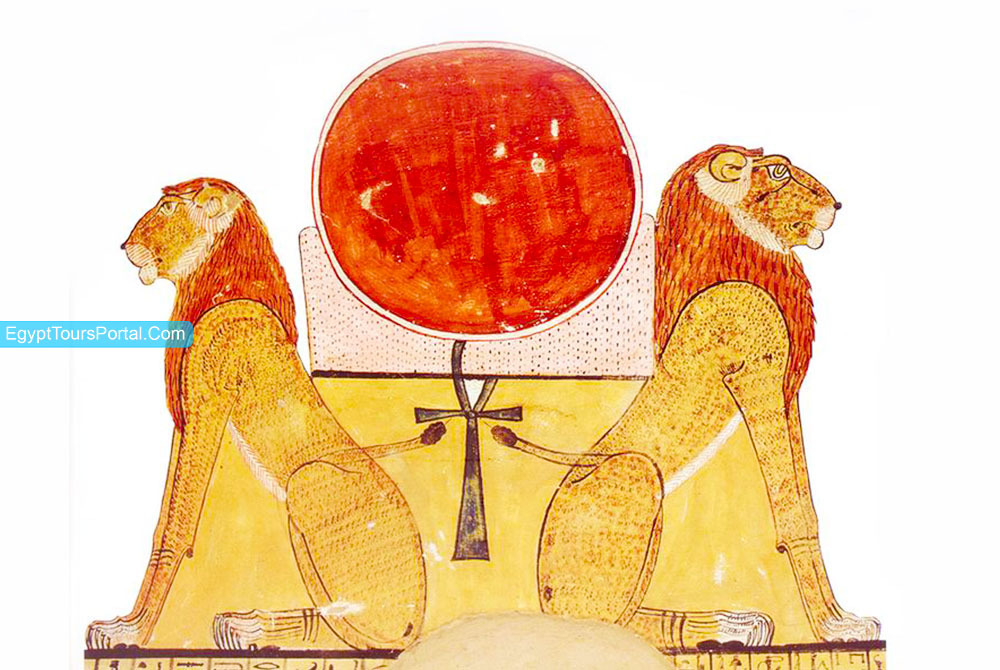

The Ahket Symbol is a concept of the horizon that completes the symbol Djew of the mountain which is seen as a magical place in the sky where the divine sun rises to spread love and life. Akhet is also the name of the inundation season when the Nile River flood water brings nutrients to all the life and plants of Egypt.
Note: The Ahket symbol was a symbol of the horizon across the beautiful and blessed landscape of Egypt made of divine waters of the Nile across the sacred sand dunes.

The powerful symbol Shu stands as the concept of air and light plus the ideal of emptiness. The feather of shu served as the name of the God Shu god of peace, air, and wind plus being one of the 9 deities of the Ennead and one of the primordial ancient Egyptian gods . The symbol stands as a representation of both day and night and the separation located between the two.
Note: The shu symbol of the embodiment of the god Shu of the air who is by far of the oldest deities of the Heliopolis cosmogony.

The mythical Duat symbol stands as a representation of the realm of the dead which is ruled by Osiris the god of the underworld plus it is the home for many gods including Osiris, Thoth, Anubis, Hathor, and Maat who also appear during the judgment process.
Note: The majestic Duat symbol is seen across temple walls as the insignia of the Underworld where the fate of every Egyptian soul is decided.
Egyptian mythology includes an infinite number of great stories to discover plus you can explore these memorable Egyptian symbols by booking unforgettable Egypt holiday packages from UK or enjoying one of the incredible Nile river cruises to observe the majestic temples of Egyptian pharaohs and witness the myths of gods and goddess.
Private 4 Days Cairo Tour Packages for British Travelers 4 days Cairo Egypt Tour package will shed ligh...
5 Days Cairo and Alexandria Tour Package For British Travelers 5 days Cairo and Alexandria tour package ...
6 Days Cairo, Luxor & Aswan Tour Package For British Travelers 6 days Cairo, Luxor & Aswan tour ...
Amazing 7 Days Cairo and Hurghada Holiday for British Travelers 7 Days Cairo & Hurghada tour package...
Egypt Tours Portal prides itself on being the best travel agency in Egypt as proven by our numerous positive reviews.
This review is a late, but I had to provide some feedback. My brother and I went on vacation in October 2022 and booked with Egypt Tours Portal. With on-line sc...Read More
My fiancé and I booked a private 5 day tour of Egypt with ETP starting in Cairo followed by Aswan, Abu Simbel and Luxor. We just got home and continue to talk ...Read More
This was the trip of a lifetime that I was able to have with my eldest son - an absolutely amazing experience. To be able to actually see the places and artifac...Read More
Highly recommend this tour company!!! Our guides, Moses, Mahmoud, Magred and Mohamed were exceptional, their knowledge of the history is more that accurate, the...Read More
Egypt Tours Portal is an excellent company to use to arrange your visit to Egypt. They work with phenomenal guides (we had Mahmoud Nour in Upper Egypt and Mohse...Read More
It was an absolutely amazing trip where we saw some of the most historical and beautiful sights in Egypt. Our tour guide Mohamed Elshemei was extremely knowledg...Read More








